Table of Contents
In simple terms, blended learning is a mix of traditional classroom teaching and online learning. It’s a modern approach that leverages the power of technology to enhance learning experiences. In the Philippines, this approach is gaining traction as a viable solution to the country’s educational challenges.
Why Discuss the Cost of Blended Learning in the Philippines?
The cost of education is a vital topic in the Philippines. As the country grapples with the need for quality and accessible education, blended learning presents a promising solution.
But what’s the cost of blended learning in the Philippines?
This question is not only relevant for policymakers and educators, but also for parents and students. Understanding the cost implications of blended learning can help stakeholders make informed decisions about its adoption and implementation.
In this post, we delve into the cost of blended learning in the Philippines, exploring its impact on the educational landscape of the country.
This is an important discussion, as the effective implementation of blended learning can significantly influence the country’s educational future.
So, let’s take a closer look at the costs and implications of blended learning in the country.
Understanding Blended Learning

Defining Blended Learning
Blended learning, as the name suggests, blends online educational materials and opportunities for interaction online with traditional classroom methods. It necessitates the physical presence of both teacher and student, with some elements of student control over time, place, path, or pace.
A good example of this is when students study theory online at home, then go to school to apply the theory through practical activities.
Blended Learning’s Emergence in the Philippines
The rise of blended learning in the country is a response to evolving educational needs. The country’s education system has been striving to enhance learning outcomes while meeting the demands of a growing student population.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this shift. As schools closed, blended learning emerged as a practical solution to continue education amidst constraints. The implementation of blended learning has not been without challenges. It has highlighted the potential of this approach in enhancing the accessibility and quality of education in the Philippines.
Nevertheless, the transition to blended learning involves costs. An understanding of these costs is crucial in planning and implementing effective blended learning strategies.
As we explore the cost of blended learning in the Philippines, we aim to shed light on its impact and potential for the country’s education system.
The Cost of Implementing Blended Learning
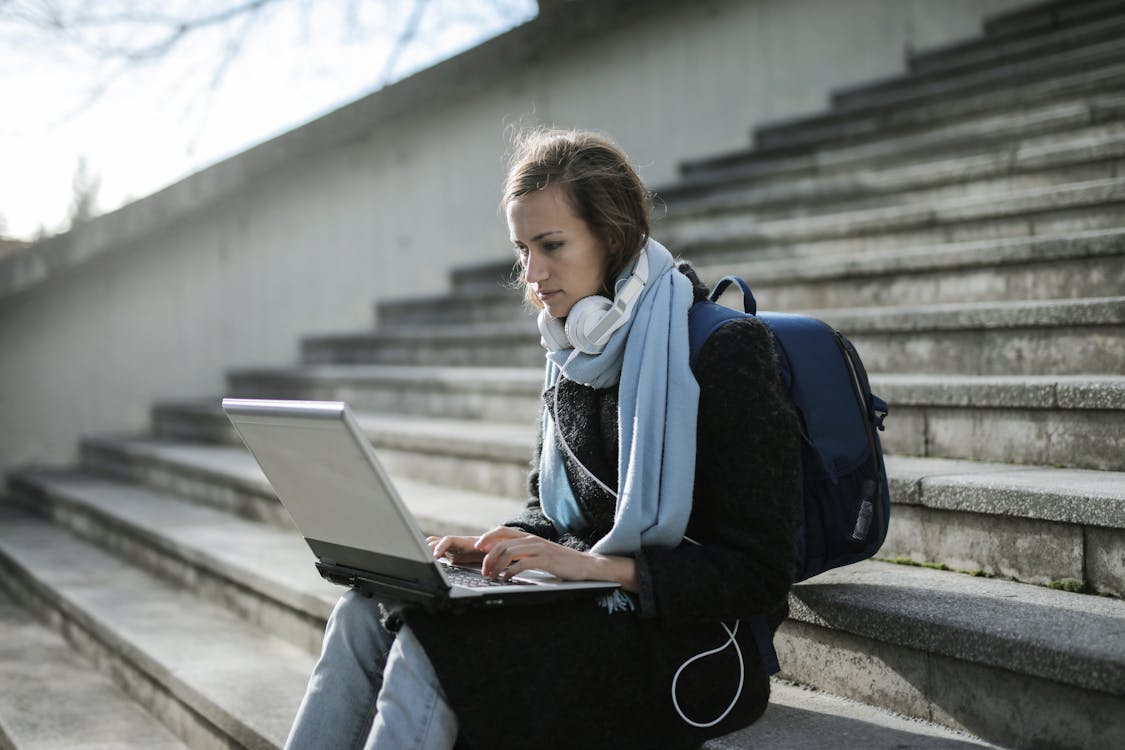

Technological Infrastructure
The bedrock of blended learning is technology. The shift towards this learning model requires a robust technological infrastructure.
This implies a significant investment in hardware such as computers, tablets, and servers.
Furthermore, it necessitates reliable internet connectivity—a challenge in many rural parts of the country.
Thus, the cost of establishing and maintaining this infrastructure is a critical factor in the implementation of blended learning in the Philippines.
Educational Materials
Modern learning requires a shift in educational materials, with a greater emphasis on digital content. The costs associated with this shift include the development or procurement of online learning platforms, digital textbooks, and interactive content.
These costs can be substantial, but should be viewed as long-term investments that can enhance the quality of education.
Training for Teachers
Teachers play a critical role in this type of learning. They must be equipped with the necessary skills to facilitate online instruction and use digital tools effectively. This requires comprehensive training programs, which add to the cost of implementing blended learning.
However, investing in teacher training is crucial to ensure the success of the blended learning model.
Implementing modern learning can be substantial. It’s essential to consider these expenses as investments in the future of education.
By understanding these costs, we can better plan for a more inclusive and effective educational system.
Benefits vs. Costs
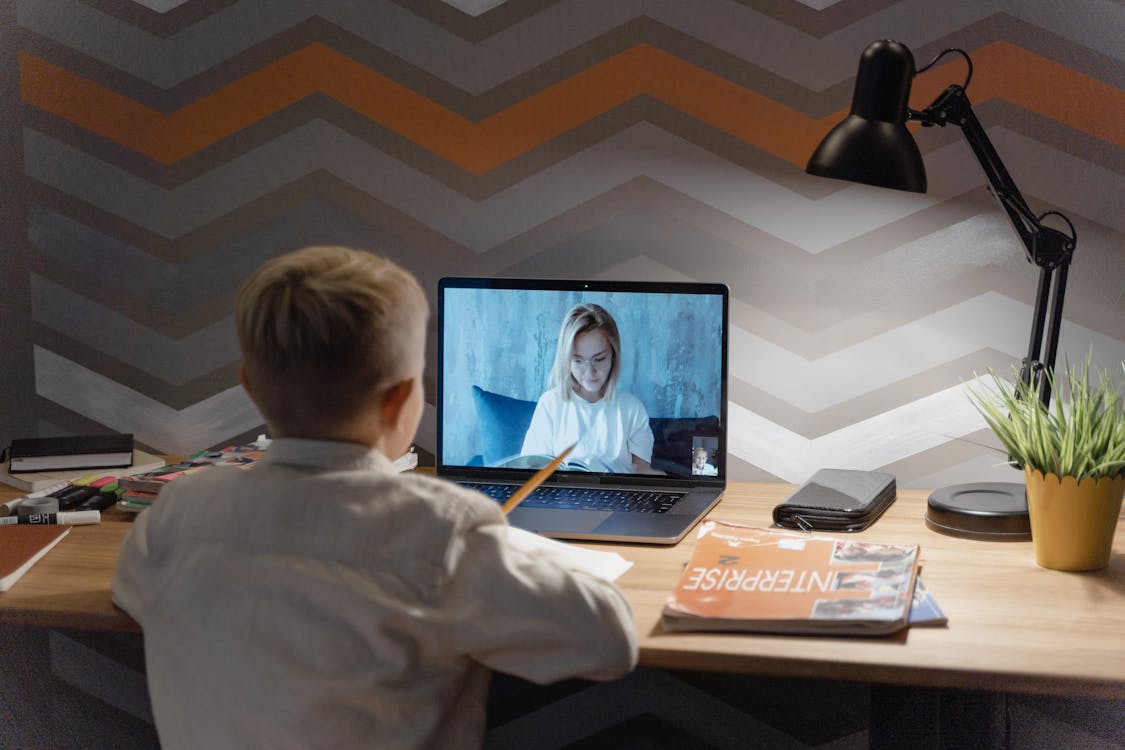

Improved Learning Outcomes
Blended learning can lead to improved learning outcomes. It provides students with a flexible learning environment that combines the best of both online and face-to-face instruction.
This model allows students to learn at their pace, which can lead to better comprehension and retention of the material.
Despite the cost of implementing blended learning, the potential for improved educational outcomes makes it a worthy investment.
Accessibility and Reach
Online components of blended learning make education more accessible. This model can reach students in remote areas, where traditional classroom settings may not be available.
In the Philippines, where geographical barriers can limit access to education, the reach of blended learning is a significant advantage.
The cost of blended learning may be offset by its potential to provide education to a larger number of students.
Cost Comparison: Traditional vs. Modern Learning
When comparing the cost of traditional and blended learning, several factors come into play. Traditional education has its expenses, such as building and maintenance costs, transportation, and physical materials.
On the other hand, blended learning requires investment in technological infrastructure, digital materials, and teacher training.
However, eventually, the digital resources used in blended learning can be updated and reused, potentially leading to cost savings.
In essence, while the initial cost of setting up blended learning might be high, its benefits such as improved learning outcomes and wider reach make it a worthwhile investment.
Additionally, the potential for long-term savings should not be overlooked.
Shifting from traditional classroom settings to blended learning may present challenges, but the experiences of many students adapting to online classes in the Philippines demonstrate its feasibility and potential benefits.
Government and Private Sector Initiatives

Funding and Support for Blended Learning
Recognizing the potential of blended learning, both government and private sector entities in the Philippines have made efforts to support its implementation.
Government initiatives include funding for technological infrastructure, teacher training, and digital materials. This commitment demonstrates the recognition of the impact of blended learning on education and the desire to manage the cost of education.
Private sector entities, including corporations and non-profit organizations, have also stepped in to support blended learning. This includes providing financial resources, technical support, and educational materials.
These initiatives are crucial in helping schools transition from traditional classroom settings to online classes.
Success Stories of Cost-effective Blended Learning Programs
There are numerous success stories of cost-effective blended learning programs in the Philippines. These stories serve as proof of how students adapt to blended learning and the positive impact it can have on education.
For example, one program in a remote area successfully implemented a blended learning model with minimal resources, leveraging local community support and using innovative low-cost solutions.
These success stories demonstrate that with creativity and community involvement, the cost of implementing blended learning can be managed effectively.
In summary, the transition to blended learning in the country is supported by various government and private sector initiatives. The success stories of cost-effective blended learning programs serve as inspiration for other communities and institutions to follow suit.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, the shift towards blended learning comes with costs. These include the need for technological infrastructure, educational materials, and teacher training.
However, the impact of blended learning and its potential to transform education in the country is undeniable.
Despite the challenges, students are adapting to blended learning, proving that a shift from traditional classrooms to online classes is possible.
The Future of Blended Learning in the Country
Looking forward, the future of blended learning is bright. With ongoing support from both the government and private sectors, and the demonstrated success of cost-effective programs, the prospect of widespread blended learning becomes even more feasible.
This shift could redefine the cost of education in the Philippines, making quality education more accessible to all.
While the journey to fully implement blended learning is far from over, the potential benefits for students, teachers, and communities are vast. The blend of traditional and digital teaching methods could lead to improved educational outcomes and greater opportunities for personal growth and development for students across the country.
As we move forward, let’s embrace the change, adapt, and see how blended learning can shape the future of education in the Philippines. It’s a journey worth taking.






No Comment! Be the first one.